

Since 0.002 parts- per-million corresponds to the area under the standard normal distribution curve that lays outside of the ± 6 SD distant from the mean. Statistically however, 6 sigma corresponds to 0.002 DPMO rather than 3.4 DPMO. Quantitatively, the performance of ‘‘world-class’’ processes is 6 sigma, which implies that only 3.4 or less DPMO are expected to occur. This is quantified through the sigma metric (SM), which can directly provide the number of defects per million opportunities (DPMO) ( 1). Through their combined use, the Six Sigma process aims to achieve very small output imprecision, such that 12 standard deviation (SD) units can be fit between the upper tolerance limit (UTL) and the lower tolerance limit (LTL) ( i.e., 6 SD can be fit between the target and the UTL/LTL). Six Sigma is based on two important principles: 1) problem-solving approaches, such as define, measure, analyse, improve, and control (DMAIC) improvement cycle, and 2) quantitative statistical analysis. The Six Sigma methodology represents an evolution in quality management that has been widely implemented in industry, healthcare, and laboratory medicine. Additionally, 1.5 SD shift should not be considered as a constant parameter automatically included in all calculations related to SM. To ensure that the SM value accurately reflects process performance, we concluded that a 1.5 SD shift should be used where it is necessary and formally appropriate. This causes great deviation of the SM from the actual level.
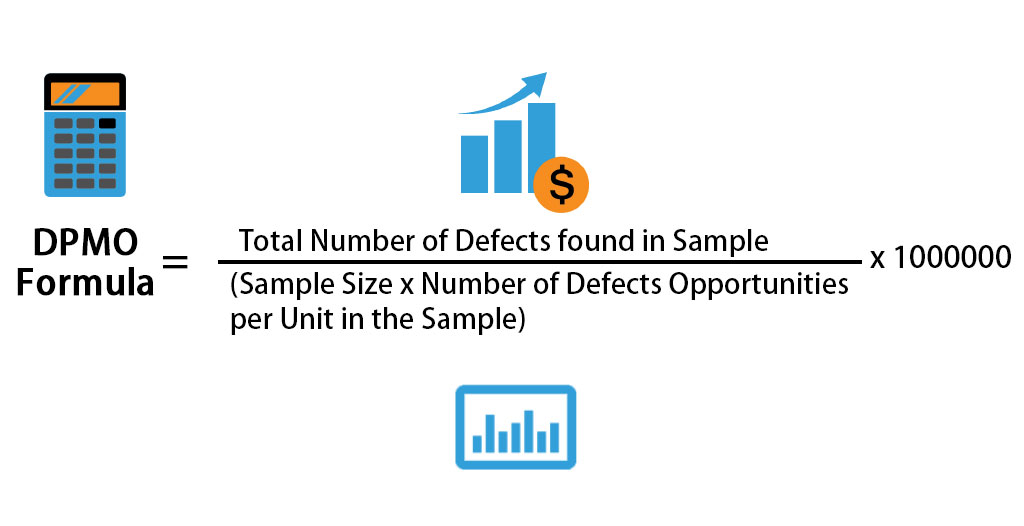
In contrast, a 1.5 SD shift should be taken into account for normally distributed data, such as the analytical phase of the total testing process in practice, this shift has been included in all type of calculations related to SM including non-normally distributed data.
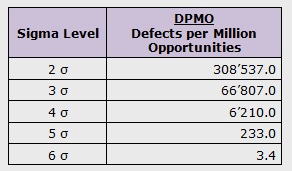
The reason for this difference is the introduction of a 1.5 standard deviation (SD) shift to account for the random variation of the process around its target. However, statistically, 6 sigma corresponds to 0.002 DPMO rather than 3.4 DPMO. The performance of a process is evaluated by the sigma metric (SM), and 6 sigma represents world class performance, which implies that only 3.4 or less defects (or errors) per million opportunities (DPMO) are expected to occur. The Six Sigma methodology has been widely implemented in industry, healthcare, and laboratory medicine since the mid-1980s.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
